Intelligent Video Analytics: The Vision of Tomorrow
A White Paper on AI-Powered Video Analytics by Pensees Singapore

There are about one billion surveillance cameras installed globally as of 2021. This number is only expected to grow, with governments and private firms around the world adopting newer forms of video surveillance technology. Singapore, where Pensees Systems Pte Ltd is based, is one of the most surveilled countries in the world according to Comparitech. In line with the government's plans, Singapore's closed-circuit televisions (CCTVs) are expected to increase to over 200,000 by 2030, with over 90,000 already installed.
What is Video Analytics?
Video Analytics refers to the leveraging of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyse video content to detect and identify people, objects, changes in environment and presence of anomalies.
Without Video Analytics, video surveillance systems remain dependent on human monitoring, recording footage without providing any additional insights. In these cases, CCTV cameras are just passive devices, like ‘having eyes but not brains’. With Video Analytics, AI algorithms are deployed to analyse footage in real time, identifying occurrences that require human attention and sending alerts for timely action. With Video Analytics working automatically 24/7, you can actualize “Virtual Patrolling” without needing to deploy manpower on-site. AI-enabled Digital Transformation Platforms connected to CCTV cameras are highly promoted by the Singapore government as well as abroad, both to improve productivity and solve the manpower crunch, and also to bring convenience and peace. This plan is in line with the rapid advancement of initiatives such as Smart Cities, Smart Buildings, Smart communities and Smart Factories.
The capabilities of Video Analytics can be classified into four broad categories:
-
Detecting people or objects, as necessary.
-
Identifying the subject, either human via face or other subjects.
-
Classifying the subject based on its traits, actions, and so on.
-
Tracking the person or object’s motion. This can even be done across multiple cameras, leveraging the interconnectivity of CCTV systems.
Diagram showing the four main capabilities of Video Analytics

Though Video Analytics may often be associated with CCTV and security systems, its capabilities and benefits extend far beyond this area. For example, in factories or construction sites, dangerous actions and breaches of safety guidelines can be detected. In public spaces, safe distancing guidelines can be enforced. Businesses can track crowd movement, demographics, and volume to improve operations. Car licence plates can be identified and tracked in carparks to improve management of parking resources.
The multitude of capabilities and opportunities that Video Analytics presents will undoubtedly continue to expand its usage by both governments and businesses in the foreseeable future.
How does Video Analytics work?
Video Analytics leverages AI algorithms, as well as current or new video surveillance infrastructure such as digital IP camera networks to enable autonomous detection of events, people or objects.
AI-Powered Video Analytics
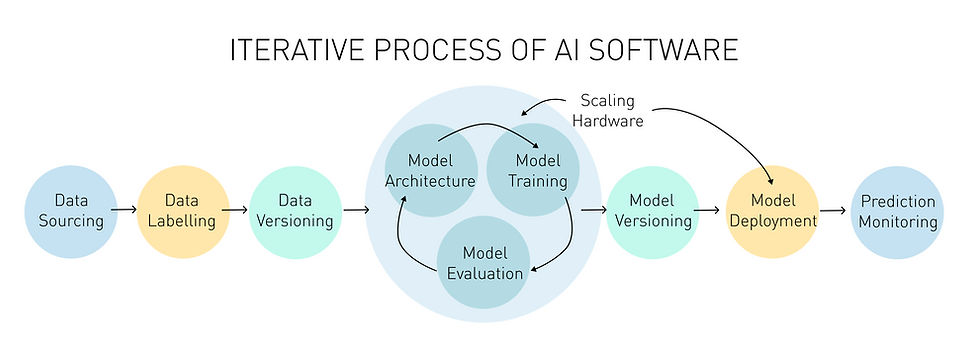
What differentiates AI software from traditional software is its iterative process. Deployment of the model in production is not the end of the process. Instead, there is a need for regular collection of relevant data, training and evaluation of the model, and this cycle will repeat until the required accuracy has been achieved.
Diagram showing the iterative process of AI software. (Ng & DeepLearningAI, 2021)
AI-powered Video Analytics can be powered by two types of AI algorithms:
1. Machine Learning
2. Deep Learning

Process of Traditional Machine Learning and Deep Learning
1. Machine Learning
In the machine learning process, data is collected as raw input, collected and labelled based on features. Then, After an iterative training process, a fully-trained traditional machine learning model becomes the program, which can then be used to produce output in the form of event and image detection and identification in AI-powered Video Analytics. In traditional machine learning, fixed and handcrafted features are used instead of automatically learned features from given data, which fails to achieve the best performance and accuracy most of the time.
As the algorithm continues to perform its function with data given, it learns and improves over time. In cases where the algorithm returns inaccurate predictions or classifications, however, human intervention is still required.
2. Deep Learning
Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning, and is a breakthrough technology moving machine learning closer to the intelligence of human brains.
An article by the MIT Technology Review describes Deep Learning to be a software that “attempts to mimic the activity in layers of neurons in the neocortex, the wrinkly 80 percent of the brain where thinking occurs. The software learns, in a very real sense, to recognize patterns in digital representations of sounds, images, and other data.” In the same way, deep learning algorithms learn through example, though at this stage of technological development, the number of examples far outweighs that which humans require.
Deep learning features are learned automatically and adaptively from big data. During the training phase, a Deep Neural Network (DNN) is fed thousands of labelled images as raw input, which the algorithm will learn to classify. When an input image is shown to the algorithm, the layers in the neural network respond to increasingly complex shapes and structures, comparing them with the training data. Finally, it will produce an identification of the image. The same applies for video data. As such, being able to automatically define what features to look for, and whether these features come in a chained set, deep learning has the ability to detect and classify more complex objects.
While making predictions and classifications, the algorithm of a deep learning model is able to determine whether or not it is accurate enough using its own neural network, without the need for human intervention.
Not only has deep learning been applied in areas of image recognition and video analytics, it has also been deployed for functions such as image enhancement, speaker ID, audio classification, unconstrained fingerprint recognition, 3D reconstruction, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), translation, and even self-driving cars.
As deep learning technologies continue to advance, machine learning and Artificial Intelligence will be brought closer to the goal of matching, and in some cases, even surpassing the abilities of the human brain.
Edge-Based Analytics and Cloud Analytics

Video Analytics can operate based on edge-based analytics or cloud analytics.
Edge analytics refers to Video Analytics that operates on the camera end, in other words, at the ‘edge’ of the network. The surveillance camera itself is equipped with the technology to analyse the footage in real-time and create metadata.
As everything is done on-site, it results in lower latency and does not require network connectivity to the Cloud. Therefore, it is suitable for processing time-sensitive data. The lower levels of bandwidth Edge analytics requires also makes it suitable for usage in remote locations. However, it requires more storage capacity and advanced surveillance camera infrastructure.
Due to limited processing power of edge devices such as AI-enabled cameras, video analytics functions which can be embedded in low-end edge devices would either be smaller models or less comprehensive functions. Additionally, such devices are also susceptible to low accuracy and poor robustness due to the usage of fixed models without the flexibility to fine-tune for various use cases.
Cloud analytics refers to Video Analytics that operates on a Cloud platform. Therefore, video footage is sent in real-time to the Cloud platform, where it will be comprehensively analysed by various video analytics models. The algorithm will immediately produce best performance and accuracy, where fine-tuning or online learning can be carried out to adapt to new environments.
The centralised nature of the Cloud allows the metadata and footage to be accessed from anywhere at any time, and scalability allows for greater storage space for footage, snapshots and data. Additionally, Cloud-based video analytics is compatible with any camera, leveraging on existing infrastructures. Therefore, this eliminates the need for new hardware. However, it is not recommended in areas with weak connectivity, as it requires high levels of bandwidth and faster connection speeds.
What can Video Analytics do?
Video Analytics technology has various capabilities, including but not limited to:
● Face recognition
● Facial expression, body posture and gaze analysis
● Recognition and documentation of person attributes such as hair colour, skin colour and type of clothes
● Detection of age and gender
● Detection of anomalous human behaviour such as fighting, loitering, smoking, falling and climbing
● Detection of mask on human face
● People counting of crowds, entry and exit
● Measurement of distance between humans and/or objects
● Recognition and documentation of object attributes, such as make, model and colour of a car
● Detection of anomalous changes in environment (e.g. unattended objects, fires)
● Detection of text (Optical Character Recognition - OCR), including licence plates of vehicles
These capabilities, and many more, have been harnessed by different industries for various applications. Read on to find out more about usage examples of AI-Powered Video Analytics.
Use Cases and Applications of Video Analytics
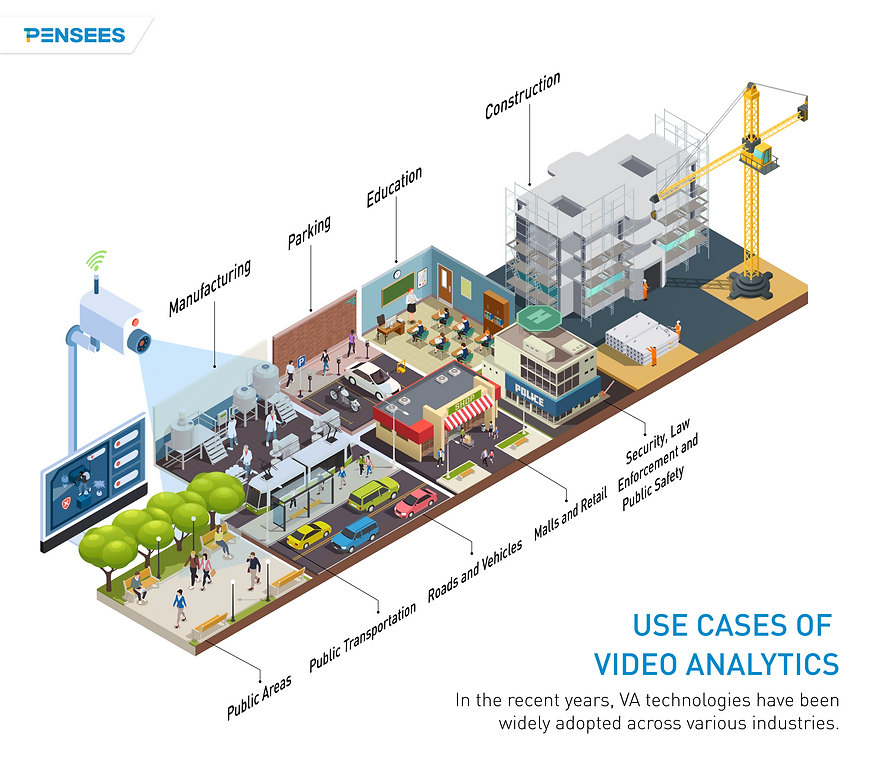
Be it to provide timely security alerts, valuable insights or data to streamline operations, Video Analytics is widely used across various industries and applications.
Security, Law Enforcement and Public Safety

Video Analytics transform CCTV cameras into intelligent systems. Given that CCTV cameras are most commonly used for security purposes, the introduction of VA brings a variety of functionalities and benefits for investigation and deterrence.
Using AI algorithms, Video Analytics is able to detect actions such as fighting, loitering, intrusion, trespassing, crowd, illegal gathering and so on, as well as anomalies such as unattended objects. By automatically extracting information on potential security and then alerting the relevant security personnel. These detections take place 24/7, providing seamless intelligent surveillance.
By automatically comparing and matching physical features with information stored in databases, facial recognition and identification of detailed attributes of people can assist police and security in tracking and locating suspects, criminals or missing persons. Even if there is no pre-existing information in databases, re-identification of individuals can be performed, tracking individuals and their movement paths across footage captured in different times and locations, providing a comprehensive understanding of their movements and activities. Video Analytics is also sensitive enough to re-identify the same individual even if clothing or accessories are changed.
In recent years, Video Analytics for law enforcement and public safety is no longer limited to CCTV cameras in fixed locations. Companies have rolled out autonomous patrol robots equipped with Video Analytics technology to allow for more mobile and flexible security solutions to further complement the effort of law enforcement and security services.
Construction Sector

With face recognition technology and intelligent video analysis of human behaviour, rapid warnings will be triggered when dangerous operations, falling-over risks and deviation from pre-set routes are identified in the course of construction work. Using intrusion detection, it will also be able to pinpoint break-ins to restricted areas in construction sites, alerting relevant personnel to take timely action. The People Counting function of Video Analytics can also be deployed in construction sites to ensure personnel limits in designated areas, making sure that these limits are neither exceeded, nor is the area left unsupervised and unattended.
Analysis of site footage can also provide insights on productivity and progress tracking for zones or buildings, allowing for better decision-making for managers.
Public Areas
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for social distancing. Video Analytics has been adapted to suit this need with the capability of social distance management in public areas where people tend to congregate. Even as the pandemic comes to a close, this technology remains practical for controlling crowd density in crowded areas or events such as sporting events or concerts to allow for safety and a better experience.
Malls and Retail
Aside from the usual security and surveillance functions, Video Analytics can also be deployed in the retail industry to understand their customer demographics, preferences and purchasing habits.
Age and gender detection allows for easier visitor profiling, allowing retailers to understand the demographics that visit their malls or stores. Time spent in-store as well as queue times can also be tracked, and busy periods with high numbers of customers can be highlighted for efficient allocation of manpower. Person re-identification can be utilised to identify returning customers and performance can be further improved with transfer learning technology. The combination of these information and more help retailers obtain a comprehensive picture of their customer base, forming the basis for predictive analytics to prevent stock and manpower shortages, pointing the way for future decision-making. Mall operators can also track movements between stores, measure engagement with pop-up retail events, monitor usage of common areas and assess suitability of mall layouts.
As shopping continues to move online, brick-and-mortar retailers and mall operators place greater emphasis on providing pleasant and unique customer experiences that cannot be replaced by online shopping platforms. Video Analytics proves to be a valuable tool in retail to understand consumer behaviour and preferences, giving retailers the opportunity to capitalise on this advantage in an informed and flexible way.
Public Transportation

Due to the complexity of public transportation systems, public transportation companies and police departments have difficulty identifying pickpockets, dangerous personnel, and those involved in illegal activities. Video Analytics with behaviour recognition technology monitors the actions of passengers, ensuring that any violations or suspicious behaviour such as smoking, climbing over barriers and loitering are immediately detected and alerted to security for action to be taken.
Face capture data of all people on board can also be uploaded and compared with information in an existing key personnel pool in the database through the intelligent comparing function of VA, enabling automatic analysis and detection of criminal suspects without the need for constant staff monitoring.
Unattended objects are a major security issue for public transportation. Video Analytics can be employed for the identification of unattended objects, notifying staff for necessary action. Coupled with the captured face and person attributes, the owner of the unattended object can also be identified and contacted.
On a larger scale, captured data can be analysed by VA to obtain the number of passengers boarding and alighting at each station, as well as the flow of their movements and transfers, allowing for section flow data and visual display of various passenger flow indicators. By collecting, integrating, analysing and applying passenger big data, strong decision support can be provided for dispatching resources and public transport scheduling for public transport operators, thereby optimising the operations of public transportation. This results in the twofold benefit of economic benefits and increased passenger satisfaction.
Roads and Vehicles

In recent years, an estimated 70% of illegal and criminal cases involve vehicle driving. Public security checkpoint systems and CCTVs are commonly installed along roads and expressways, and it is necessary to explore the value of the massive amount of data collected. Video Analytics for vehicle big data solutions is able to identify characteristics of vehicles such as type, brand, colour and so on even when the vehicles are driving at high speeds, and then automatically extract effective information. Driver behaviours can also be detected and analysed, such as not wearing seatbelts or using mobile phones when driving. By linking the data of the vehicle owner and vehicle, real-time warning for high-risk vehicles and behaviours can be provided. Criminals can be tracked with the retrieval of data and comparison with existing databases based on time intervals, points ranges, licence plate numbers, ID numbers, and so on, swiftly identifying suspicious vehicles amidst the large amount of information.
In real-time, Video Analytics can also detect and record the violation of traffic rules of both drivers and pedestrians, such as illegal U-turns, failure to conform to traffic lights, tailgating, jaywalking and so on.
By analysing big data acquired from Video Analytics of traffic security footage, insights on driver and pedestrian habits and preferences are easily collected, supporting urban planning and route improvements in future.
Parking
Video analytics of CCTV camera footage is capable of Licence Plate Recognition (LPR), which records the make, model, colour and other information of cars found to be parked at restricted areas. Video Analytics’ LPR capabilities also enables numerous functions for smart parking systems, such as zone-based parking, implementation of VIP and blacklist, and so on.
Video Analytics has been utilised in carparks of various buildings and industrial parks, with Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) of vehicle licence number to identify vehicles of tenants and contractors. With parking lot reservation and integration with the operator’s car park kiosk, it allows drivers to search the parking zone of their vehicles for greater convenience.
Manufacturing
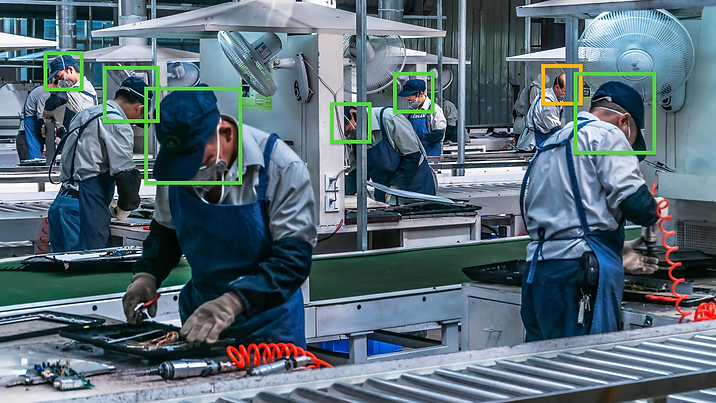

With Video Analytics, digital and visual supervision for employees all across the workplace can be enforced. Video Analytics recognize the arm, leg, foot, head and body behaviour of each employee within the view of video surveillance cameras, identifying dangerous operations as they occur. This allows for intelligent prevention of safety accidents, where a rapid warning will be triggered when illegal operations, falling over risks and other dangerous behaviours take place. As such, personnel will be able to take measures in a timely manner to avoid production accidents, providing assurance and convenience for enterprise security management.
With intelligent video analysis technology, the system can also identify ill-disciplined employee behaviour, such as playing with mobile phones, sleeping and leaving the post without permission. This provides digital evidence for employee performance evaluation, alleviating the workload of enterprise management and reducing management costs. This data can be further harnessed by generating employee performance indicators, calculation models and so on, providing further insights for management to improve the efficiency of their operations.
Video Analytics technology has been implemented in a large manufacturing firm covering an area of 3,500,000 square metres with staff strength of 28,000. To date, the intelligent VA for manufacturing management has identified and warned 160 violations during the manufacturing process and noticed by managers for timely intervention, effectively avoiding occurance of safety accidents and achieving an impressive rate of zero production safety accidents.
Education
Video Analytics and be utilised on campuses for monitoring key areas like libraries and dormitories to carry out early warning of unauthorised personnel through face recognition. Suspicious personnel loitering outside schools can also be detected for security staff to take prompt action. Based on the structured data collected by VA systems, big data analysis technology is then used for pre-event perception, in-process follow-up and post-event retrieval.
These functions help fill security gaps in schools, providing a safer learning environment for students and greater reassurance for parents and teachers with smart campus security.
The surveillance system with VA can also detect and send alerts for inappropriate behaviour of students, such as fighting, climbing over fences, and so on. Falling and fainting can also be alerted for action to be taken. The comprehensive monitoring scope of Video Analytics alleviates the burden of teachers and school staff, improving the discipline and wellbeing of students without the need for additional manpower or patrol time.
Video analysis is the answer to data-based campus management, helping to transform the current mode of campus management to one that is more efficient and information-based. With data processing for movement trajectories, entry and exit times, as well as activity hours and areas of the student population, insights can be generated for future decision-making on resource allocation, activity planning, and so on.

Benefits of Video Analytics
The efficiency and convenience and Video Analytics can bring about a range of benefits to organisations, including but not limited to:
● Enhanced security
● Improved safety in daily operations
● Reduces human error
● Reduces manpower costs due to less personnel needed to monitor footage
● Enables more efficient usage of manpower
● Improves personnel response time
● Increases likelihood for crime detection and prevention
● Increased operational efficiency and economic gains from insights
What are the limitations of Video Analytics?
Despite being a powerful tool, as with any technology, Video Analytics has its inherent limitations.
Real-world data is always changing. Therefore, when the data used to train machine learning models in AI Video Analytics systems cannot keep up with the fast-changing data input, low accuracy during deployment will occur. This is referred to as ‘data drift’.
Thus, it is crucial to ensure that the algorithm is regularly refreshed and updated with the latest data. Time has to be taken to collect large amounts of data for Deep Learning, annotate the data, as well as train and fine-tune the model before deployment of subsequent versions.
The effectiveness of Video Analytics can be limited by the quality and resolution of surveillance video footage, which is dependent on the camera image and video quality. This is especially crucial under low lighting, extreme weather conditions, or when identifying a subject from a long distance. Even an effective VA algorithm may be undermined by poor camera image quality.
The same applies for unsuitable settings of the surveillance camera. For instance, overly long shutter speeds may lead to overly long exposure times, causing motion blur in footage or images, especially at night or in low light conditions. Though longer exposure times also maximise the amount of light reaching the camera and therefore improve image clarity, there needs to be a balance in parameters to achieve the ideal footage and images. Therefore, in order to maintain and maximise the effectiveness of your VA system, it is recommended to consult video analytics experts, or the supplier of your surveillance camera or Video Analytics system if you encounter any issues with video footage.
Video Surveillance VS Video Analytics: What's the difference?

Video Surveillance refers to the monitoring of a certain area, building or facility using image and video data captured with surveillance cameras. Video surveillance systems often consist of a network of closed-circuit television (CCTV) or Internet Protocol (IP) cameras, monitor displays, and recorders. The video footage can be monitored live in control rooms or remotely by security guards and staff. The footage can also be recorded for future reviewing. Certain video surveillance systems may be configured to only begin recording when movement is detected, enabling personnel to review the footage afterwards.
Video Analytics, also known as Video Content Analysis, refers to real-time analysis of video footage such as video footage from surveillance cameras, to identify events, images and occurrences. Video Analytics is able to work autonomously to detect pre-assigned temporal and spatial events without constant human monitoring, and is able to notify users of the type of event as they happen without requiring manual review of the footage. Video Analytics is built on existing video surveillance infrastructure.

The main differences between Video Surveillance and Video Analytics
Computer Vision VS Video Analytics: What’s the difference?
Computer Vision is a type of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in which models are trained to analyse, identify and classify images in photo, video and 3D formats. It aims to emulate and replicate human vision with computers, extracting useful information from image(s).
Computer Vision is used in Video Analytics, and in fact forms its foundation. However, Computer Vision also has many other applications, such as image recognition and categorization, text detection (Optical Character Recognition), 3D model generation, and so on.
Video Analytics, also known as Video Content Analysis, refers to real-time analysis of video footage such as video footage from surveillance cameras, to identify events, images and occurrences. It makes use of computer vision and deep learning to live and recorded video footage to enable detection.
The Video Analytics Market and Industry
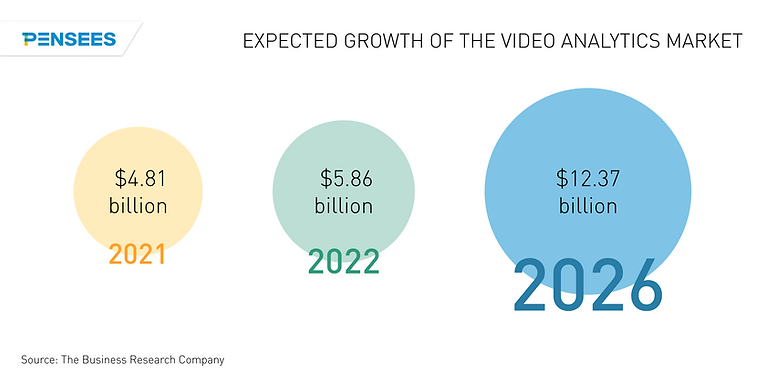
As of the second quarter of 2022, based on a report by The Business Research Company, the global video analytics market is expected to grow from $4.81 billion in 2021 to $5.86 billion in 2022 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.8%. The market is expected to grow to $12.37 billion in 2026 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.5%.
Among the major trends driving Video Analytics technology worldwide are smart city plans, increased safety concerns, a shift from analog closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras to digital IP cameras and the availability of high-resolution cameras. The rise of 5G networks allows for secure connectivity of more devices, high-quality media transfer and ultra-low latency, improving camera responsiveness in real-time monitoring and allowing for the implementation of Video Analytics systems in more remote areas. The global COVID-19 pandemic has increased demand for and acceptance of crowd monitoring and face mask detection technologies, and paves the way for widespread and accelerated adoption of Video Analytics technology in the following years. According to Fortune Business Insights, in the post-pandemic era, rising demand for real-time event detection is likely to drive market growth in the VA industry.
Can Video Analytics replace human intelligence?
Deep learning algorithms for Video Analytics have been developed by emulating neuron networks in human brains, and are able to make categorizations and predictions based on big data. While algorithms can be trained and fine-tuned by themselves, collecting data and annotations remain dependent on humans, since only humans are acutely aware of real-world changes. Without retraining initiated by humans, Video Analytics algorithms are still vulnerable to data drift and other forms of inaccuracies at the current level of technology.
Future developments for Video Analytics: What's Next?

Greater interconnectedness will enable Video Analytics on a larger scale. With increased interconnectedness between buildings, security systems and so on, Video Analytics can be leveraged to generate more extensive insights and form a stronger safeguard for security.
There is a potential for Video Analytics systems to be integrated with other systems, such as building management systems, access control and intruder detection. Instead of working in traditional siloes, Video Analytics can form a part in an integrated solution for improved security. Therefore, in addition to improving the accuracy and range of video analysis, interoperability is another area that Video Analytics companies will have to focus on for long-run relevance. Artificial Internet of Things (AIoT), with an embedded algorithm in various products, presents a promising direction for VA companies to develop towards, as well as an opportunity for organisations wishing to take the lead in optimising their operations and security in a more holistic manner.
About Pensees Singapore
Pensees is a company with an internationally-leading AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) ecological platform. We take “AI is a service” as our mission and transform cutting-edge AI technologies into evolving inclusive intelligent services.
We have leveraged a closed-loop model of AI, IoT, and SaaS to provide AIoT devices, cloud services, and scenario-based AIoT solutions in fields of smart cities, intelligent residential communities, intelligent businesses, and more, so as to promote the industrialization of AI. At present, Pensees has customers from 50+ cities in China and Singapore, and accommodates online stable operation of 100,000+ AIoT front-end devices.
Find out more about our company and technology here.